With the growing number of seniors and their desire to “age in place,” there’s been a demand for home healthcare services. The Baby Boomer generation is fueling this increase. Seniors want to maintain some of their independence, while also having some of their healthcare needs met in the comfort of their own home. Understanding the numbers behind this “senior boom” is key to figuring out the impact on the healthcare system as a whole.
Demographic Shift: Aging America in Numbers
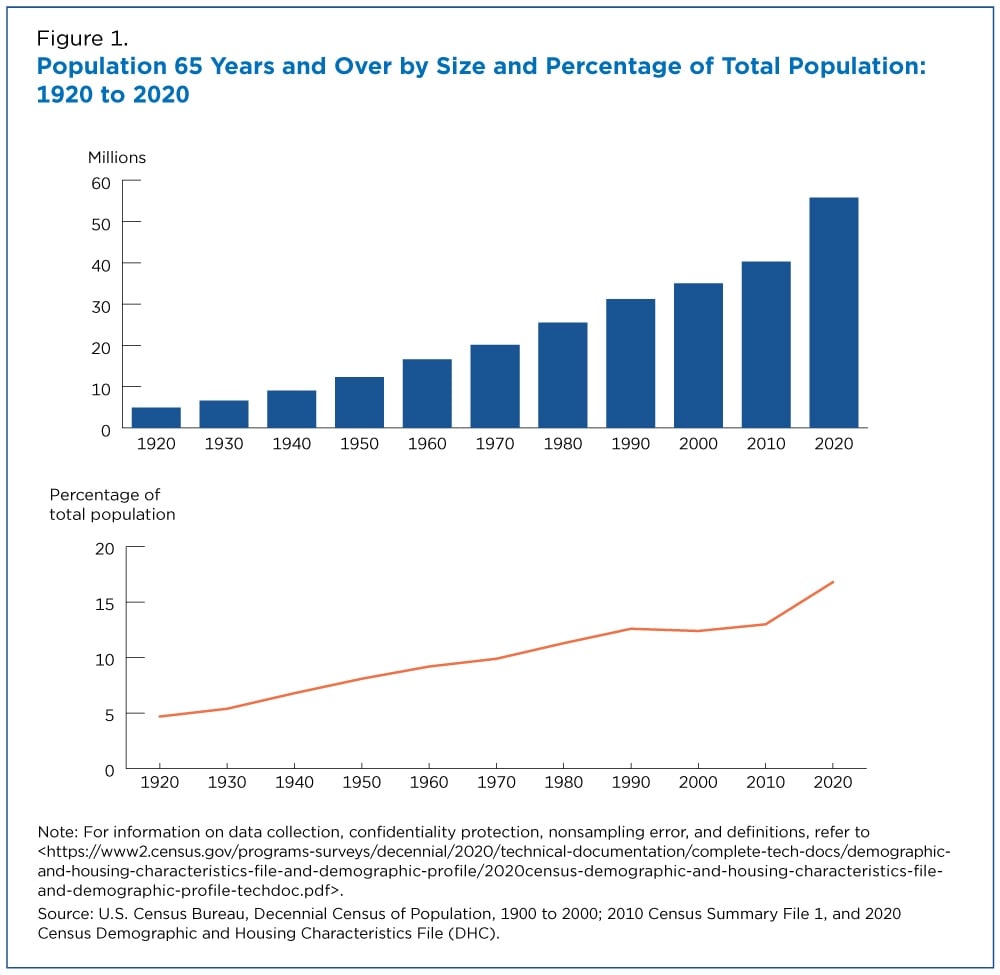
The U.S. senior population is growing at a rate that is unprecedented in our history. According to the United States Census Bureau, “In 2020, about 1 in 6 people in the United States were age 65 and over. In 1920, this proportion was less than 1 in 20.”
This rapid growth is mostly attributed to the Baby Boomers generation, who began turning 65 in 2011. The senior population is only projected to continue to increase. According to the Urban Institute, “The number of Americans ages 65 and older will more than double over the next 40 years, reaching 80 million in 2040.”
Older Americans aren’t just increasing in population numbers, but they’re also living longer. According to the Urban Institute, “In 1960, men who turned age 62 could expect to live another 15 years. By 2040, they will likely live for another 22 years.”
These trends underscore a dramatic shift: more seniors living for longer periods, who will increasingly require ongoing care.
Rise in Seniors’ Desire to “Age in Place”
Seniors increasingly want to stay in their own homes as they age and maintain a level of their independence. According to AARP’s 2021 Home and Community Preferences survey, “Over three-quarters (77%) of adults age 50 and older want to remain in their homes as they age. This desire is consistent across the lifespan with 63% of adults overall saying the same.”
This desire to “age in place” comes with recent data that more seniors are capable of handling a lot of their lifestyle needs. According to The Population Reference Bureau, “More older adults can meet their daily care needs. Older adults are functioning better on their own, and a shrinking share are living in nursing homes and assisted living settings than a decade ago. Home modifications and assistive devices such as walkers have helped older Americans maintain their independence.”
Although many seniors can handle daily living tasks, they may need some healthcare assistance for chronic conditions, which has led to a rise in home care or personal care services.
Increasing Demand for Home Healthcare Services
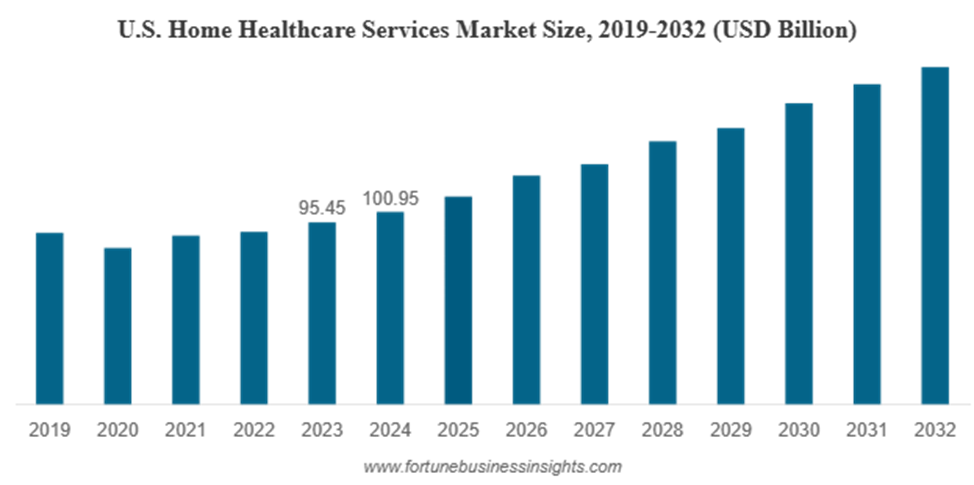
The demand for home healthcare services is rapidly increasing, driven by both demographic shifts and economic considerations. The U.S. home healthcare sector is on track to reach $176.3 billion by 2032, driven by the expanding senior population.
Job Growth
According to a job outlook forecast from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Employment of home health and personal care aides is projected to grow 17 percent from 2024 to 2034, much faster than the average for all occupations.” This exponential growth reflects the rising need for in-home support.
“Between 2022 and 2032, the direct care workforce is projected to add just over 860,000 new jobs, which represents the largest growth of any job sector in the country,” according to PHI.
The surge in demand highlights the critical need for skilled workers to meet the healthcare needs of a growing aging population.
Cost Comparison: Home Healthcare vs. Nursing Home Care
Home healthcare also offers a cost-effective alternative to nursing home care, often providing high-quality services at a fraction of the expense.
According to AARP, “Home care is more affordable than nursing homes, which have an annual average cost of $108,000 for a private room, but it still exceeds what many older households can afford to pay with their income.”
However, it’s important to note that the cost-effectiveness of home healthcare can diminish if around-the-clock care is required. Additionally, while home healthcare offers flexibility and the comfort of remaining at home, nursing homes provide a higher level of medical supervision and social interaction, which may be necessary for individuals with complex health needs.
Can Home Healthcare Reduce Hospital Readmissions?
Moreover, studies have shown that receiving care at home can reduce hospital readmissions, improving patient outcomes while easing the strain on the healthcare system.
Regency Health Care states, “For instance, an analysis of Medicare data revealed a linkage between the average length of service (ALOS) from home health agencies and lower rates of acute care hospitalization (ACH). Moreover, longer home health intervention duration tends to correlate with significant reductions in readmissions”
According to The National Library of Medicine, “Achieving a sustainable reduction in readmissions requires a holistic and patient-centered approach considering the multifaceted factors contributing to this issue. Ultimately, the success of these efforts not only benefits individual patients but also leads to the overall cost-effectiveness and efficiency of the healthcare system.”
This growth in the home healthcare market shows a lot of potential but also underscores a critical worker gap that can threaten agencies’ ability to scale.
Financial Pressure for Home Healthcare Agencies
Home healthcare agencies today face mounting financial pressures as they navigate a rapidly growing market. The costs of providing quality in-home care continue to rise, driven by factors such as higher wages for skilled caregivers, training expenses, and the need for specialized equipment.
At the same time, agencies are grappling with workforce shortages, as the demand for caregivers increasingly outpaces supply, impacting the level of care seniors receive. Adding to these challenges, delayed payments from Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers can create significant cash flow gaps.
Rising Costs of Home Healthcare Services
According to AARP, “Home care cost increased in 47 states between 2019 and 2021, with 23 states showing more than a ten percent increase in cost relative to income. On average, the annual per person cost of home care in 2021 was roughly $42,000 a year (for 30 hours of weekly care at $27 per hour)—more than 20 percent higher than in 2019.”
The cost of providing home healthcare services has been steadily increasing, driven by rising wages for skilled caregivers, investments in training, and the need for specialized medical equipment. Agencies must also account for transportation expenses, insurance, and regulatory compliance costs, all of which add to their financial burden. As the demand for in-home care continues to grow, these rising expenses place additional pressure on agencies to maintain high-quality care.
“About 70 percent of American adults aged 65 and older will need some form of long-term care in the future,” according to the Administration for Community Living. This rising aging population in the United States is driving up the costs of nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and home healthcare agencies.
Rapid Growth vs. Worker Shortages
The home healthcare industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging population and a preference among seniors to “age in place”.
In 2025, the U.S. home care market is projected to generate over $107 billion in revenue, reflecting a substantial increase in demand for home-based services. Employment in the field is also expanding, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 17% growth in home health and personal care aide positions from 2024 to 2034, much faster than the average for all occupations.
However, this rapid expansion is met with a significant workforce challenge. The caregiver shortage is a pressing issue, with approximately 718,900 openings for home health and personal care aides projected each year over the next decade.
This workforce gap not only affects the quality of care provided but also places financial strain on agencies. With high turnover rates and recruitment challenges, agencies must invest in competitive wages, training, and retention strategies, all of which contribute to rising operational costs.
Delayed Payments from Medicare/Medicaid
Home healthcare agencies often face significant financial challenges due to delayed payments from Medicare and Medicaid. These delays can disrupt cash flow, making it difficult for agencies to cover operational costs, including caregiver wages, medical supplies, and administrative expenses.
Medicare: Under the Home Health Prospective Payment System (HH PPS), Medicare pays a predetermined rate for a 30-day period of home health care. However, payment cycles can vary. While some agencies report receiving payments within 30 days, others experience delays, especially when claims require additional documentation or are subject to audits. The Patient-Driven Groupings Model (PDGM), implemented in 2020, has introduced complexities that can further extend payment timelines.
Medicaid: Payment timelines for Medicaid services vary by state, with some states experiencing longer delays than others. For instance, in certain states, home and community-based services (HCBS) waiver applicants have reported approval times averaging 89 days. Once approved, reimbursement rates can differ significantly across states, affecting the timeliness and adequacy of payments.
These delayed payments can strain home healthcare agencies, especially smaller providers with limited financial reserves.
What Does PRN Funding Do?

PRN Funding is a financial services company specializing in supporting healthcare providers, including home healthcare agencies, by helping them maintain steady cash flow and manage operational challenges. PRN Funding focuses exclusively on the healthcare industry, bringing 25 years of experience and a deep understanding of the unique financial pressures agencies face.
For home healthcare agencies, PRN Funding provides tailored financial solutions that allow agencies to pay staff on time, cover operational expenses, and invest in growth opportunities without disruption. By offering reliable funding options, PRN Funding helps agencies bridge the gap created by delayed insurance reimbursements, rising costs, and workforce challenges.
What’s the Economic Impact of the Senior Boom?
The aging population is poised to have a profound economic impact, particularly on the home healthcare industry. Spending on home healthcare services is expected to rise dramatically in the coming decades as more seniors choose to age in place. Estimates suggest that the U.S. home healthcare market could exceed $176 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of over 7%, according to the North American Community Hub Statistics.
The senior boom is also driving substantial job creation in the home healthcare sector. Employment for home health and personal care aides is projected to grow 17% from 2024 to 2034, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding hundreds of thousands of new jobs nationwide, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Beyond economic growth, expanding home healthcare services can alleviate pressure on hospitals and the broader healthcare system. By enabling seniors to receive care in their homes, agencies help reduce hospital readmissions, lower emergency room visits, and manage chronic conditions more effectively. This shift not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to a more efficient and sustainable healthcare system, benefiting both providers and the public.